How to Build a Modern Revenue Data Stack for Funnel Visibility
- Integrate everything: Connect lead and customer data across systems for a unified view.
- Establish a warehouse: By Series B, centralize your data to build a reliable source of truth.
- Automate pipelines: Use ETL/ELT tools and workflow automation to reduce manual work.
- Create actionable dashboards: Build BI dashboards that drive decisions and conversations.
- Prioritize data hygiene: Clean data fuels trusted insights — governance matters from day one.
Why Your Data Stack Matters for Funnel Visibility
Building the right team and structure is step one — but modern RevOps tooling and data infrastructure are the backbone of true funnel visibility.
Many Series A startups survive on spreadsheets and CRM hacks.
But as you scale, manual workarounds break down and fragmented data kills decision-making.
A modern revenue data stack ensures that no matter where an event happens — form fill, sales call, product usage — it flows into a centralized system that drives insights and action.
Core Components of a Modern Revenue Data Stack
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Your CRM is your system of record for pipeline management.
Configure your CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot, etc.) to match your funnel stages — and train your team that if it's not in the CRM, it didn't happen.
Prioritize a CRM that becomes your single source of truth for customer and deal data.
2. Marketing Automation and Attribution Tools
Tools like Marketo, HubSpot Marketing, or Pardot feed your top-of-funnel efforts.
Focus on:
- Seamless integration with CRM
- Consistent UTM tracking and campaign IDs
- Moving beyond lead gen to revenue attribution
3. Data Pipelines (ETL/ELT)
Centralize your data using ETL/ELT tools like Fivetran or Airbyte
Benefits:
- Nightly syncs from CRM, marketing, product, and CS platforms
- Eliminates manual CSV exports
- Prepares for warehouse-scale data modeling
4. Business Data Warehouse
Your warehouse (Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift) is the heart of your stack.
It enables:
- Unified revenue funnel modeling
- Cross-team reporting consistency
- Advanced analytics like cohort retention and lead scoring
Invest early. Even a small warehouse setup at Series A saves massive headaches later.
5. Cross-functional Analysis
Your data should democratize visibility into key metrics across different teams.
- Executive KPI dashboards
- Sales pipeline health dashboards
- Marketing ROI and attribution dashboards
- Customer Health Score Monitors
- Product Funnel Metrics
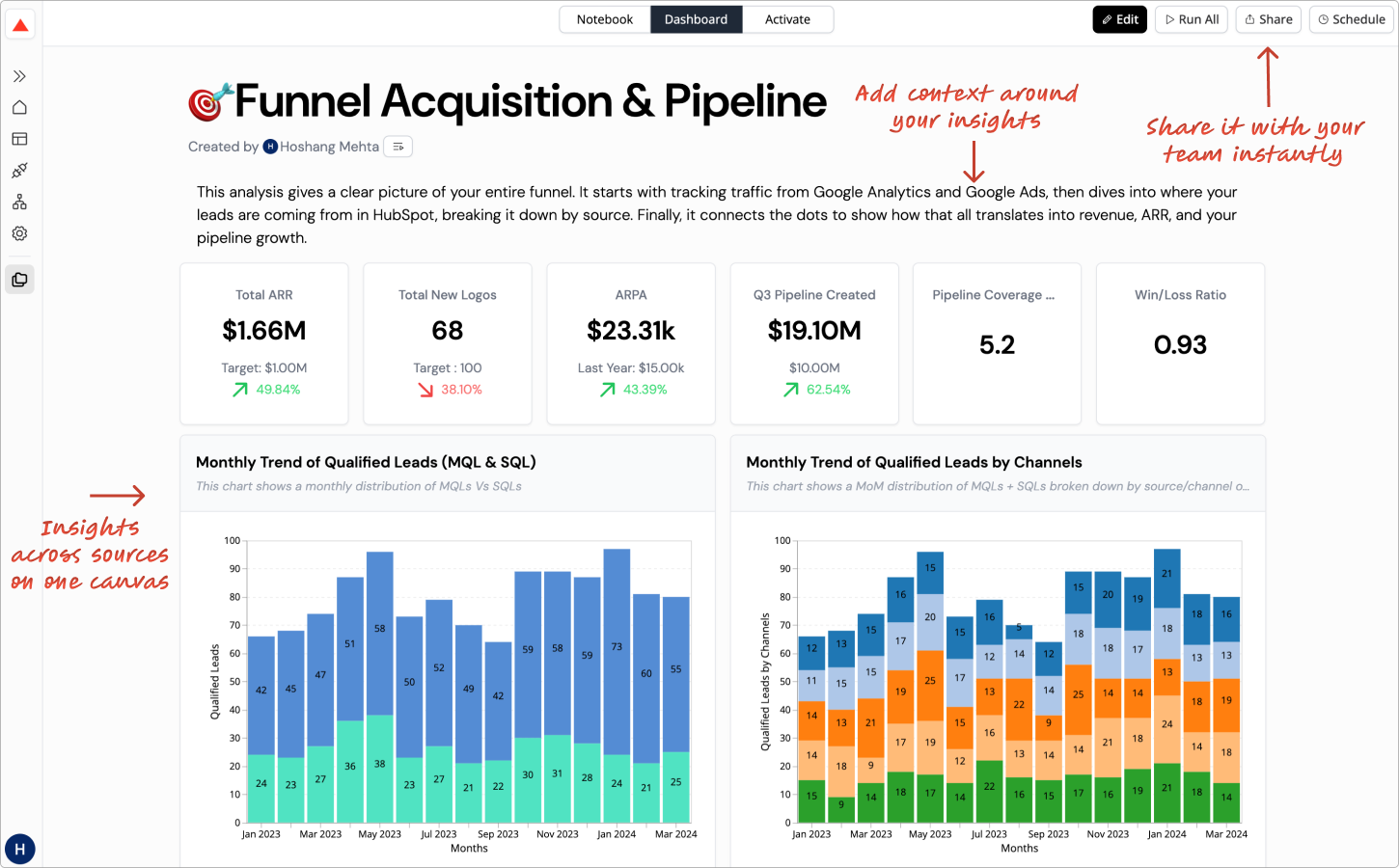 Good dashboards increase agility — leaders can react quickly based on data, not guesses.
Good dashboards increase agility — leaders can react quickly based on data, not guesses.
6. Activation Platforms and Workflow Automation
It's not enough to see data — you must act on it.
Use:
- Reverse ETL (Hightouch, Census) to push insights into Salesforce, CS platforms, ad tools
- Workflow automation (Zapier, n8n) to close integration gaps
Your goal: connected, flowing systems, not siloed tools.
7. Specialized RevOps Tools
Layer in specialized tools only when needed:
- Clari for pipeline forecasting
- Gong or Chorus for conversational analytics
- Gainsight or ChurnZero for CS insights
Audit your tech stack regularly. Cut what you don't need.
Best Practices for Building Your Data Stack
Buying all of the above tools may come with increasing costs and complexity. You can make use of modern flexible tools that handle everything from data ingestion, storage, analytics and activation in one collaborative workspace.

| Stage | Focus |
|---|---|
| Series A | Native integrations, basic CRM, outsourced data help |
| Series B | CRM + marketing automation + data warehouse + BI dashboards |
| Series C | Optimize integrations, scale automation, add predictive analytics |
Always prioritize integration, automation, and data cleanliness over shiny features.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Tool overload: Focus on solving real pain points, not buying tools for vanity.
- Poor data hygiene: Enforce governance, deduplication, and validation.
- Siloed systems: Integration is mandatory, not optional.
- Forgetting activation: Data must drive workflows, not sit idle.